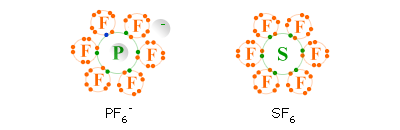
The best examples are the PF6- ( phosphorus hexafluoride or hexafluorophosphate) ion and the SF6 ( sulfur hexafluoride ) molecule whose Lewis structures are shown below.
The ground state electronic configuration of the two central atoms:
| P | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3px1 3py1 3pz1 |
| S | 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3px2 3py1 3pz1 |
In the excited state of the two central atoms above, their valence electrons are assumed to be distributed this way:
| 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 3px1 3py1 3pz1 3dz21 3dx2 - y21 |
Since six equal orbitals are required, it is assumed that sp3d2 hybridization is used to form six hybrid orbitals:
| 1s2 2s2 2p6 (sp3d2)1 (sp3d2)1 (sp3d2)1 (sp3d2)1 (sp3d2)1 (sp3d2)1 |
Geometry of PF6-
- shape of ion: octahedral
- bond angle of axial atoms: 180°
- bond angle of equatorial atoms: 90°
- bond angle between an equatorial atom and an axial atom: 90°
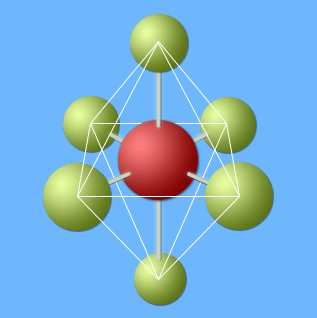
Axial atoms are in white circles; equatorial atoms are in black circles.
An octahedron is superimposed on the PF6- ion.
Geometry of SF6
- shape of molecule: octahedral
- bond angle of axial atoms: 180°
- bond angle of equatorial atoms: 90°
- bond angle between an equatorial atom and an axial atom: 90°